Diabetes & Stem Cell
How Might Stem Cells Support the Treatment of Diabetes?
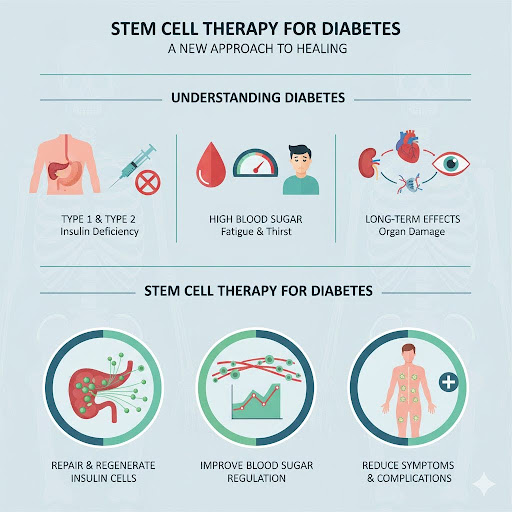
Diabetes is a serious and widespread condition in which the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This imbalance leads to elevated blood sugar (glucose) levels, which, if not managed properly, can cause a variety of symptoms and long-term health complications.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Extreme hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores
- Frequent infections
Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, potentially leading to complications such as kidney disease, cardiovascular issues, and an increased risk of infections.
Traditionally, diabetes management relies on a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and insulin therapy. While these approaches can be effective, they often require strict, lifelong adherence. Daily insulin injections may be burdensome, and medications can carry side effects—from pancreatitis to an increased risk of bone fractures. Importantly, conventional treatments manage symptoms but cannot cure diabetes or restore natural insulin production.
Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetes
Stem cell therapy offers a new approach by addressing the underlying causes of diabetes rather than just managing symptoms. Stem cells have the unique ability to transform into various cell types, regenerate damaged tissues, and restore functionality to impaired organs.
In diabetes, stem cell treatments can help:
- Promote the repair and regeneration of insulin-producing cells
- Improve overall blood sugar regulation
- Reduce symptoms and complications associated with diabetes
This therapy is a promising option for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, providing hope for patients seeking a more effective, long-term solution to managing their condition.